Artistic neural style transfer with pytorch
Published:

stylize the images with Neural networks using pytorch
you can checkout this blog on my medium page here
Earlier: The first published paper on neural style transfer used an optimization technique — that is, starting off with a random noise image and making it more and more desirable with every “training” iteration of the neural network.
Rescent: However, the technique of a subsequent paper, which is what really made neural style transfer blow up, used feedforward — train a network to do the stylizations for a given painting beforehand so that it can produce stylized images instantly using paper from Leon A. Gatys.
In this tutorial, we’ll cover how to implement the neural-style algorithm that’s based on this paper called A Neural Algorithm of Artistic Style developed by Leon A. Gatys, Alexander S. Ecker and Matthias Bethge.
for code chekout this official pytorch document here
In fine art, especially painting, humans have mastered the skill to create unique visual experiences through composing a complex interplay between the content and style of an image. Thus far the algorithmic basis of this process is unknown and there exists no artificial system with similar capabilities. However, in other key areas of visual perception such as object and face recognition near-human performance was recently demonstrated by a class of biologically inspired vision models called Deep Neural Networks.
Here we introduce an artificial system based on a Deep Neural Network that creates artistic images of high perceptual quality. The system uses neural representations to separate and recombine content and style of arbitrary images, providing a neural algorithm for the creation of artistic images. — Leon A. Gatys
What is neural style transfer?
Neural Style Transfer is a technique that can change/stylize the Input image with respect to the style given, still preserving the Content of input image.
Given an input image and a style image, we can compute an output image with the original content but a new style — Leon A. Gatys
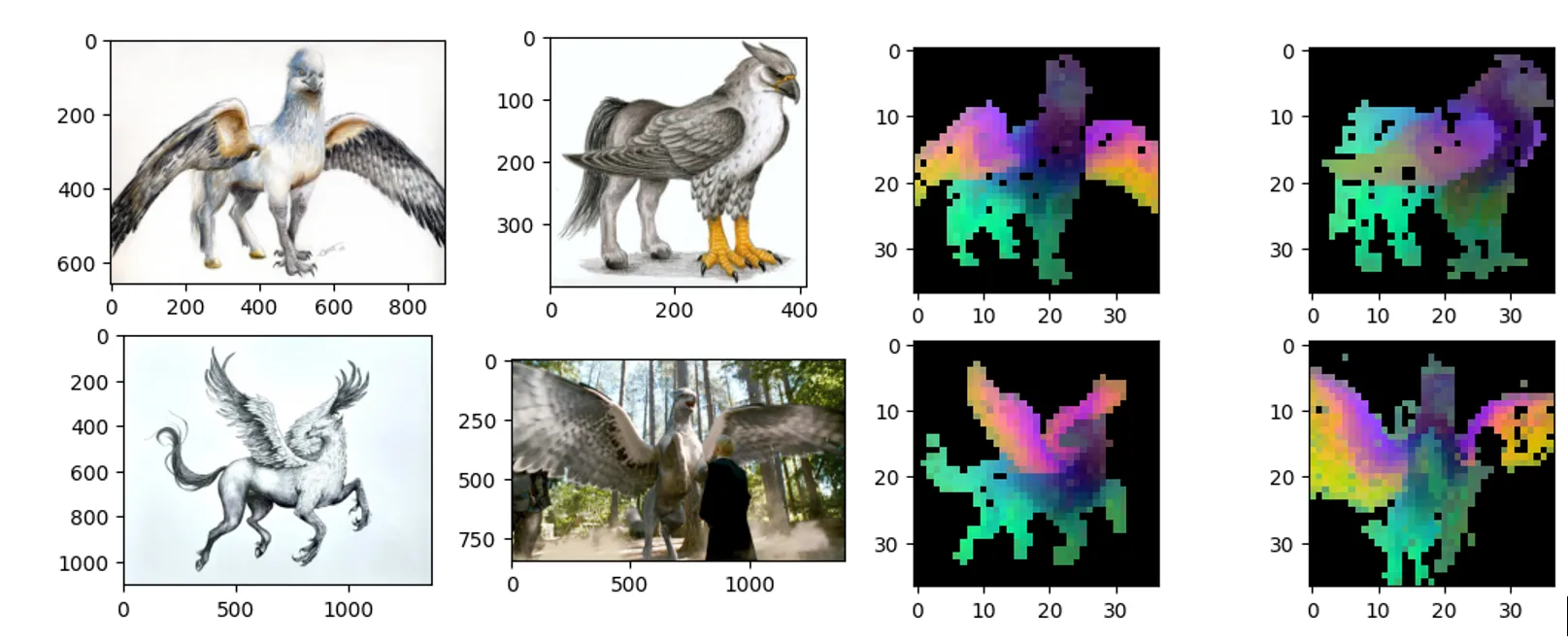
The algorithm takes 2 images, an input image/a content-image, and a style-image, and changes the input to resemble the content of the content-image and the artistic style of the style-image.

- Content image will determine how the generated image will look like. (e.g. the dog)
- Style image will give the style (or general texture) to the generated image. (e.g. style of Starry Night of Vincent van Gogh)
- Output image will have both the content from Content image and Style from styli image.(look at the figure above)
Underlying Principle
The principle is simple: we define two distances, one for the content (Dc) and one for the style (Ds). Dc measures how different the content is between two images while Ds measures how different the style is between two images. Then, we take a third image, the input, and transform it to minimize both its content-distance with the content-image and its style-distance with the style-image. Now we can import the necessary packages and begin the neural transfer.
Convolutional Neural Network:
We’re going to use a pre-trained Convolutional Neural Network such as VGG-Network because CNN is the right choice for image processing. Also, it allows us to extract separately the content and the style of an image, and that’s exactly what we want. So, we’ll pass the two images through VGG and we initialize the image to be generated at a random image.
In our model, information is so important and by using Max Pooling in CNN, we are throwing away a large number of pixel values of the previous layer and we are keeping only the highest values. So it is better to use Average Pooling because at least it uses all the data in order to get an average.
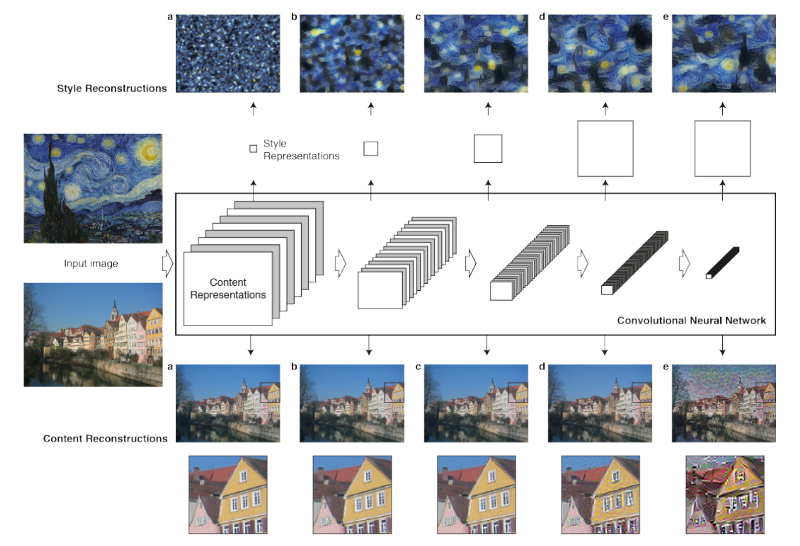
Content Reconstruction:
Our objective here is to get only the content of the input image without texture or style and it can be done by getting the CNN layer that stores all raw activations that correspond only to the content of the image. It is better to get a higher layer, because in CNN, first layers are quite similar to the original image. However, as we move up to higher layers, we start to throw away much information about the raw pixel values and keep only semantic concepts.
Style Reconstruction:
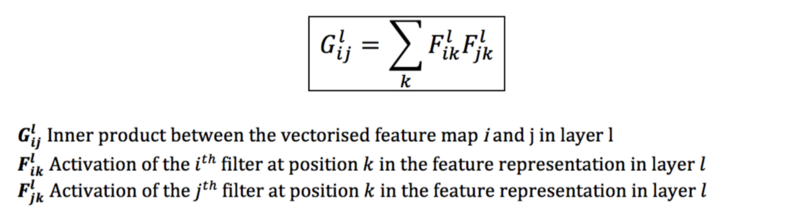
In order to get the representations of the style image, we are going to compute the correlations between different types of neurons in the network using the Gram Matrix.
So, how does Gram Matrix work?
Let’s get the convolutional features of the style image at some layer of the network. As it shows below, we’ll get a convolutional feature of volume C by H by W ( Channel by Height by Width). In other words, it’s an H by W spacial grid and at each point of it, there is a dimensional feature vector.
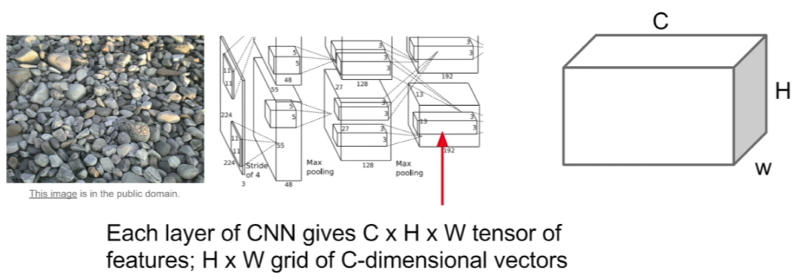
We pick out two of these different feature columns (e.g. the pink and the blue dimensional vectors), then, we compute the outer product between them. As a result, it will give us a C by C matrix that has information about which features in that feature map tend to activate together at those two specific spatial positions.
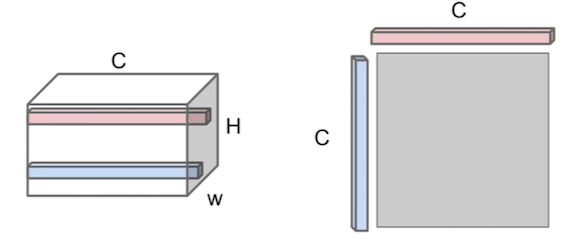
We repeat the same procedure with all different pairs of feature vectors from all points in the H by W grid and averaged them all out to throw away all spatial information that was in this feature volume.
Now, that we know how the gram matrix works, how can we compute it?
- We reshape the C by H by W tensor of features to C times H by W, then we compute that times its own transpose.
- We can also use covariance matrices but it’s more expensive to compute.
Loss function:
The loss function in style transfer is the content loss function plus the style loss function.
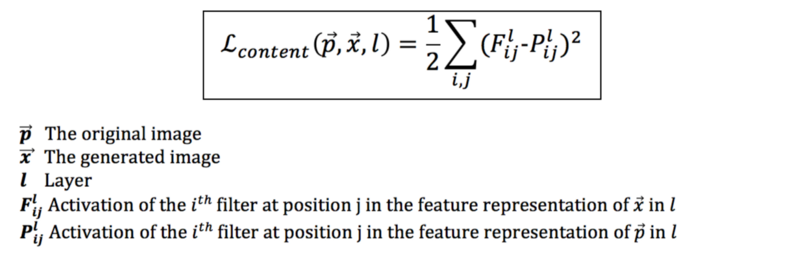
Content loss function:
It is the squared-error loss between the feature representation of the original image and the feature representation of the generated image.
We apply the content loss at one layer.
Style loss function :
First, we minimize the mean-squared distance between the style representation (gram matrix) of the style image and the style representation of the output image in one layer l.
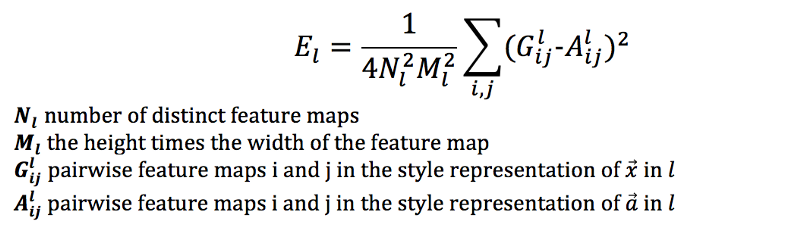
Second, we apply the style loss function on many different layers to get the total style loss:
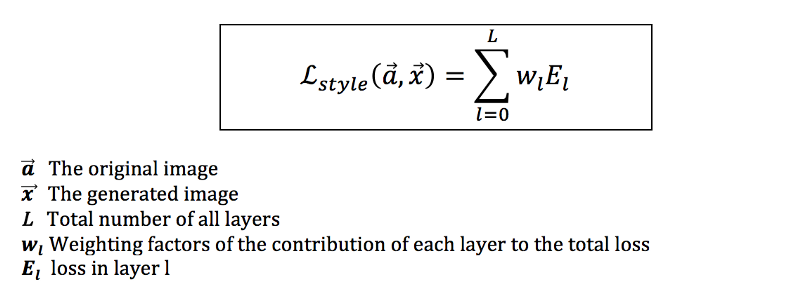
The loss of transfer learning:

We can change the hyperparameters to control how much we want to match the content versus how much we want to match the style.
Deterministic Optimizer:
In Style transfer learning, we are going to use a deterministic optimizer l-bfgs instead of Stochastic Gradient Descent or Adam because:
There is nothing stochastic here (we are not creating random mini-batches with different set of data), instead, the optimizer keeps getting the same single image.
l-bfgs determines which direction to go and the optimum distance to go in that direction by computing the hessian and doing a line search. This approach is expensive in stochastic problems but it is the right approach here.
l-bfgs does learn faster than Adam in style transfer.
All the equations in this article are from the paper Gatys, Ecker, and Bethge, “A Neural Algorithm of Artistic Style”, arXiv, 2015
Reference:
A Neural Algorithm of Artistic Style Paper here.
Official Pytorch Neural transfer tutorial here.
Thank you
thank you so much for landing on this page.