PMP course
This page has Notes from the Project Management Professional Course.
- PM- stands for Project Management
- PMO- Project Management office
- OPM- Organization project management
- KPI- Key performance Indicators
- Phasegate- untill a phase is fully completed, I can not move to the next phase in project.
Business value:
what are the project success criteria/checklist. projects end when:
- Objectives meet
- Objectives can not or will not be met
- Funds are depleted
- Need no longer exist
- Resources are no longer available.
Projects create business value:
- Tangible business value:
- Monetary assets
- stockholder equity
- market share
- Intangible business value:
- Goodwill & reputation
- Brand recognition
- benefit to public
- strategic alignment
Projects initiation Context:
- stakeholder requested for project
- technological advancement created need for new project
- crating new products, improving exisiting produts, and more
Typical Project managements:
- identifying requirements
- addressing needs, concern, rquirements of stakeholders.
- settingup, maintaining, and carrying communication.
-
balancing competing project constraints.
- Scope
- quality
- budget
- resources
- risks
PM LifeCycle:
- Idea or Concept
- Formulate the Idea
- Business case
- feasibility study
- project
- feasibility study
- Business case
- Formulate the Idea
Project Management application areas:
- Construction
- Healthcare
- finance
- IT
- Govt
- NGOs
Other areas that effect project Management:
- program management
- portfolio management
- A senior level excutive managing where & how do we invest in programs and different projects.
- portfolios are about maximizing investments.
- portfolio is collection of programs, program is collection of projects.
PMO- Project management office:
- supports project managers
- manages shared resources
- coaching, mentoring & training for project managers
- conducts project audits(to ensure whether using right tools)
- develops & maintains procedures.
- facilitates communication across different projects to speedup
Organizational Culture and Structure:
- Vision
- Mission
- Values and Beliefs
- Cultural Norms
- Hirarchy and authority
- organizational & managment style
Project Management Process:
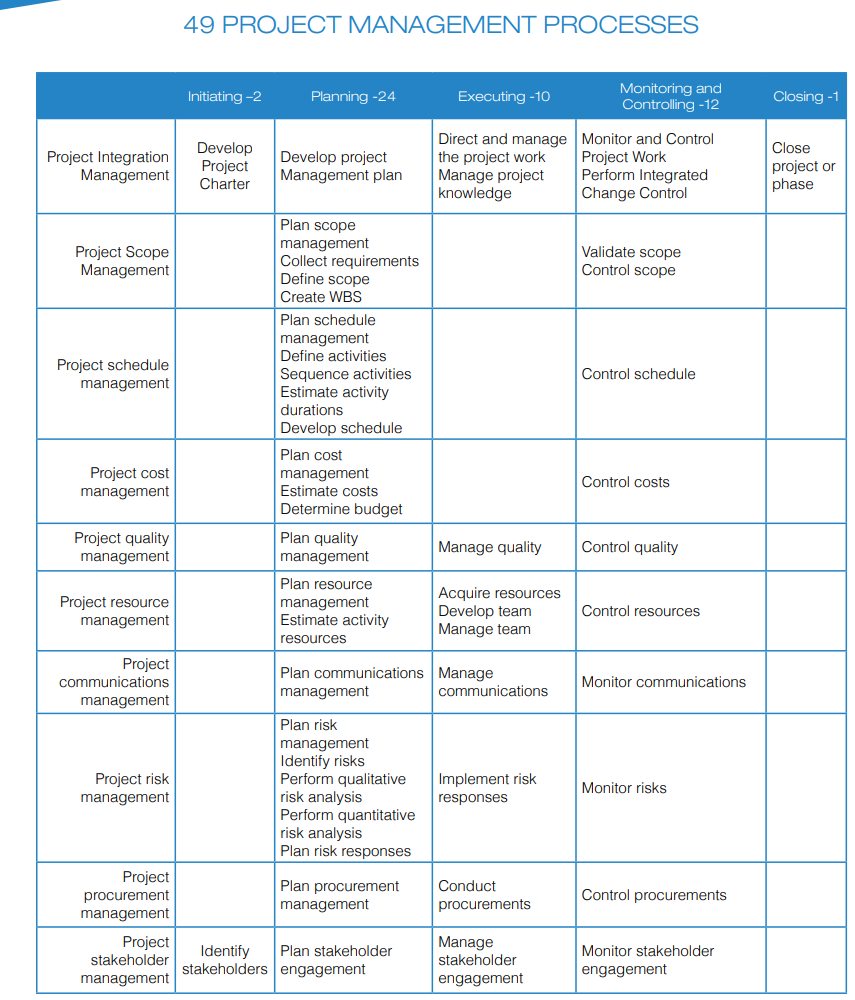
Work Performance Data:
- Raw data & facts about project.
- status of project work assignments
- percent complete
- in progress
- start & finish dates
- Data can include:
- Cost of the activities.
- no.of.change requests.
- Defects
- Duration
Work Performance Information:
- Analyzed work performance data.
- usable information to make decisions.
- status of actionable results.
Work Performance Reports:
- Work performance information in communicable form.
- Status reports
- Memos
- Dashboards
- Project updates
- helps stackholders make decision
Project Management Lifecycles:
- Predictive lifecycle
- plan-driven
- waterfall approach
- predicts the project life cycle
- changes to scope are tightly contolled
- Iterative (or) Incremental lifecycle
- iterations create deliverables(we deliver in each iteration)
- detailed scope is elaborated for each iteration.
- changes to the project scope are expected.
- Adaptive Life cycle
- change driven
- agile project managment
- rapid iterations (or) project work (or) sprint based (15 days mostly)
- backlog of requirements
- changes to the project scope are expected
Business Document for Project Management(to present to management):
- report phase-gate work
- report actual performance/costs compared to earlier business documents.
- if I did great, then cool
- if not, then create variance/exception report to report why I did not hit my KPI, why I was late or why I was over budget.
- Decision of comparision include:
- should we continue to next phase(if overcost, if too much delay,)
- end of the project
- should remain in the same phase
- repeat the phase again
Project Business case:
- economic feasibility study- is it financially profitable..?
- benefits the project creates
- project sponsor is accountable for the developement & maintainence not the manager.
- PM responsible for providing recommendations.
Business Needs:
- what is prompting the need for action
- statement document the opportunity
- stakeholders effected
- identification of the scope
Business case: project determination:
- root cause of an opportunity
- gap analysis of capabilities
- know risks
- critical success factors
- Decision criteria
Organizational knowledge repositories:
- cataloging
- archieveing
- retrievable
- Organization process Assets(the then worked team on the usecase) are part of knowlege repositories.
- archieve at closure.
- storage
- project files from past projects
- historical information and lessons learned
- issues and defect databases
- configuration management databases
- financial databases
Role of Project Manager:
- Manage things, lead people to conclusion
- getting things done
- active listener & speaker
- written & oral to internal(team) & to external(to non team and to management)
- project manage negotaites:
- aim for fair agreement
- priorities
- technical approach
- project scope
- schedule
- cost
- changes to project scope, schedule , budget
- vendor teams and conditions
- resource constraints.
- PMs solve problems
- problem definition
- RCA- root cause analysis
- treat causes, not symptoms
- Don't go to the management without a solution
Values to have to be a PM:
- knowledge: understanding project management
- performance: accomplish as a project manager
- personal: behavior, effectiveness, character, leadership
Project Documents:
